Abstract
This analysis examines the theoretical framework and methodological approach underlying the Consilience Ventures Digital Share (CVDS) valuation system, a multi-dimensional model designed to assess and optimize value creation within startup ecosystems. The framework integrates maturity assessment, dynamic valuation mechanisms, and systematic execution tracking to create a comprehensive venture evaluation paradigm.
1. Introduction
The CVDS represents a novel approach to startup ecosystem valuation that transcends traditional financial metrics by incorporating systematic maturity assessment and continuous performance tracking. This framework addresses the inherent challenges of valuing early-stage ventures where traditional discounted cash flow models prove inadequate due to high uncertainty and limited historical data.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1 Core Value Proposition
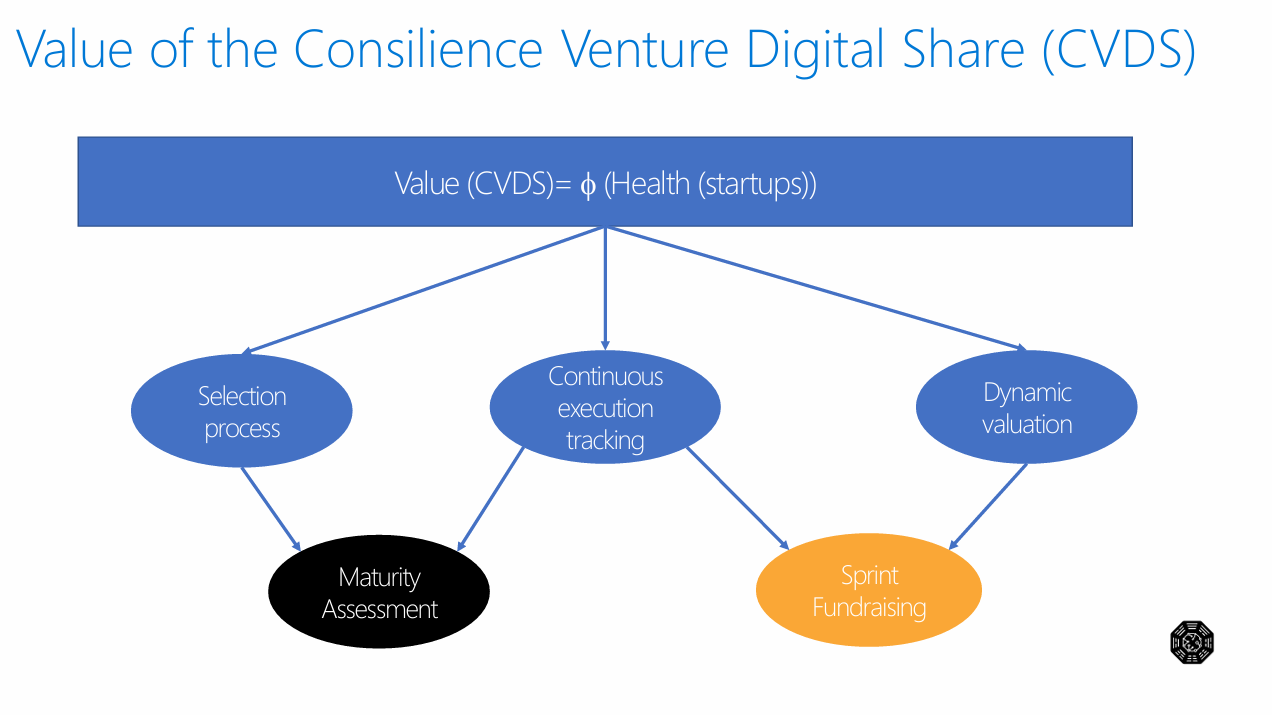
The fundamental equation governing CVDS value is expressed as:
Value (CVDS) = f(Health of startups)
This relationship establishes venture health as the primary determinant of ecosystem value, representing a departure from purely financial valuation models toward a more holistic assessment framework.
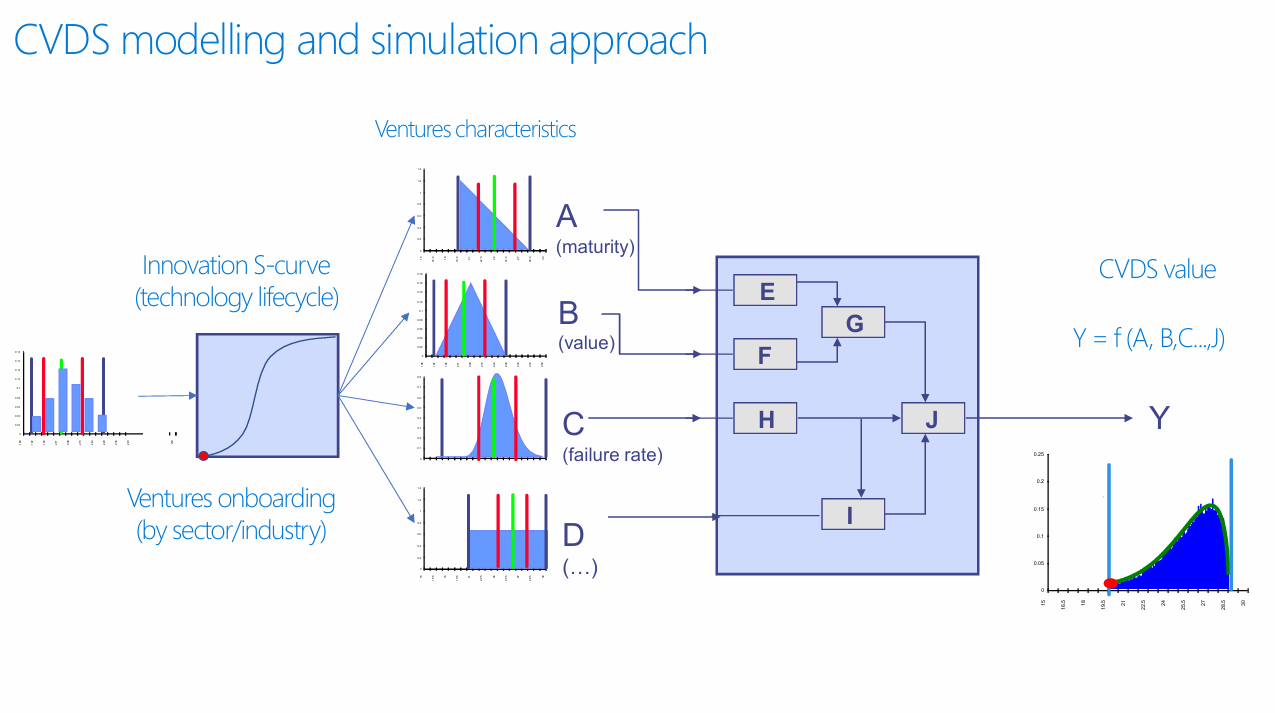
2.2 Multi-Dimensional Modeling Approach
The system employs a functional relationship:
Y = f(A, B, C, ..., J)
Where:
- A represents maturity levels
- B represents intrinsic value metrics
- C represents failure rate parameters
- D through J represent additional venture characteristics
This multi-variate approach acknowledges the complex, interconnected nature of factors influencing startup success and ecosystem value.
3. Methodological Components
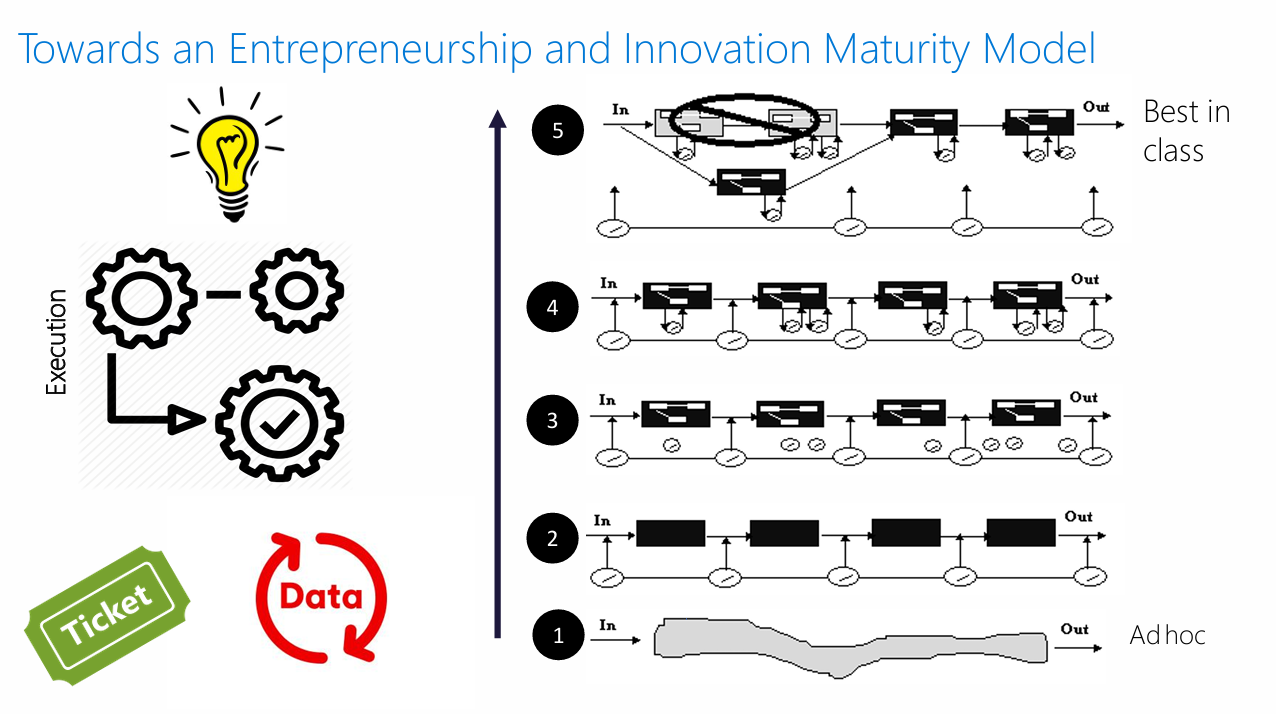
3.1 Entrepreneurship and Innovation Maturity Model
The framework incorporates a five-level maturity scale ranging from "Ad hoc" (Level 1) to "Best in class" (Level 5). This maturity assessment provides a standardized mechanism for evaluating venture development stages and execution capabilities.
Scientific Rationale: Maturity models provide structured frameworks for capability assessment and have proven effective in organizational development contexts. The application to startup ecosystems represents an innovative extension of this methodology.
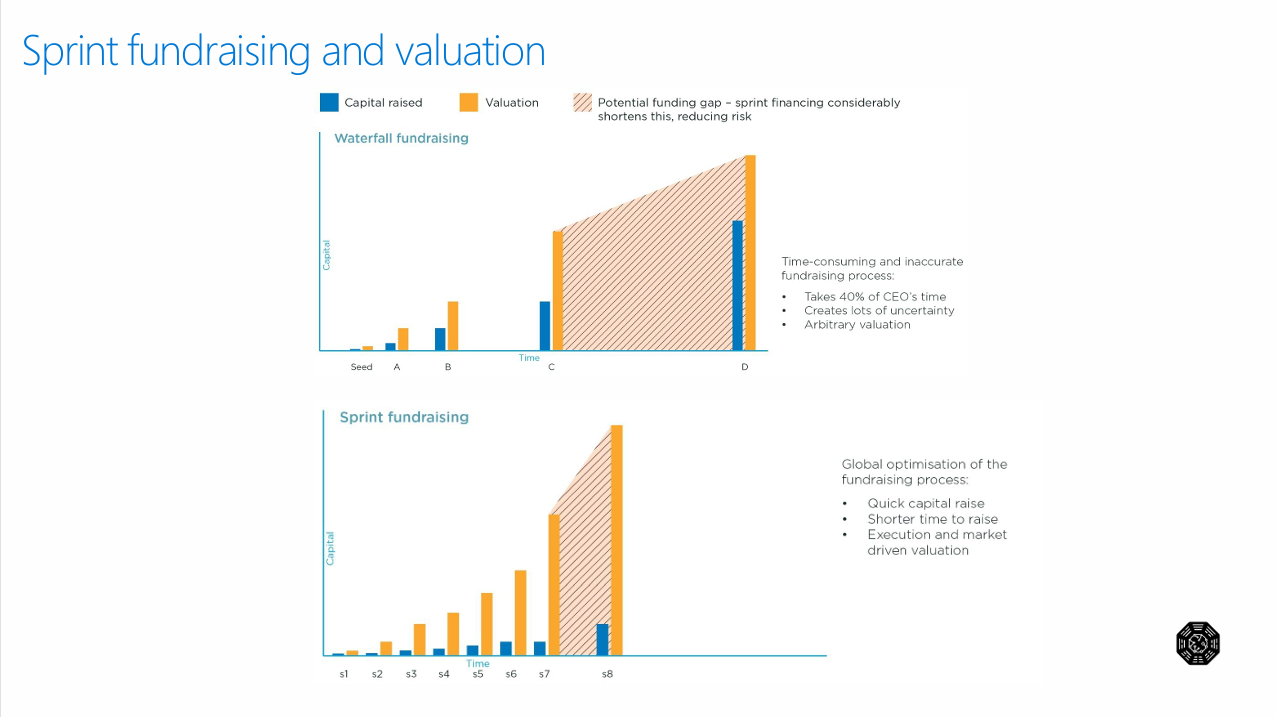
3.2 Sprint Fundraising Methodology
The integration of sprint-based fundraising aligns with agile development principles, enabling:
- Rapid capital deployment
- Iterative value creation
- Reduced time-to-market cycles
- Enhanced risk management through incremental investment
3.3 Continuous Execution Tracking
The system implements real-time monitoring mechanisms that provide:
- Dynamic performance metrics
- Early warning indicators
- Adaptive intervention capabilities
- Evidence-based decision support
4. Value Control and Assessment Framework
4.1 Dynamic Valuation Process
The CVDS employs a continuous valuation methodology that incorporates:
- Real-time venture performance data
- Market condition adjustments
- Peer comparison benchmarking
- Predictive modeling for future performance
4.2 Selection and Onboarding Process
The framework includes systematic venture selection criteria based on:
- Sector-specific evaluation metrics
- Technology lifecycle positioning (Innovation S-curve analysis)
- Maturity assessment scores
- Risk-return optimization
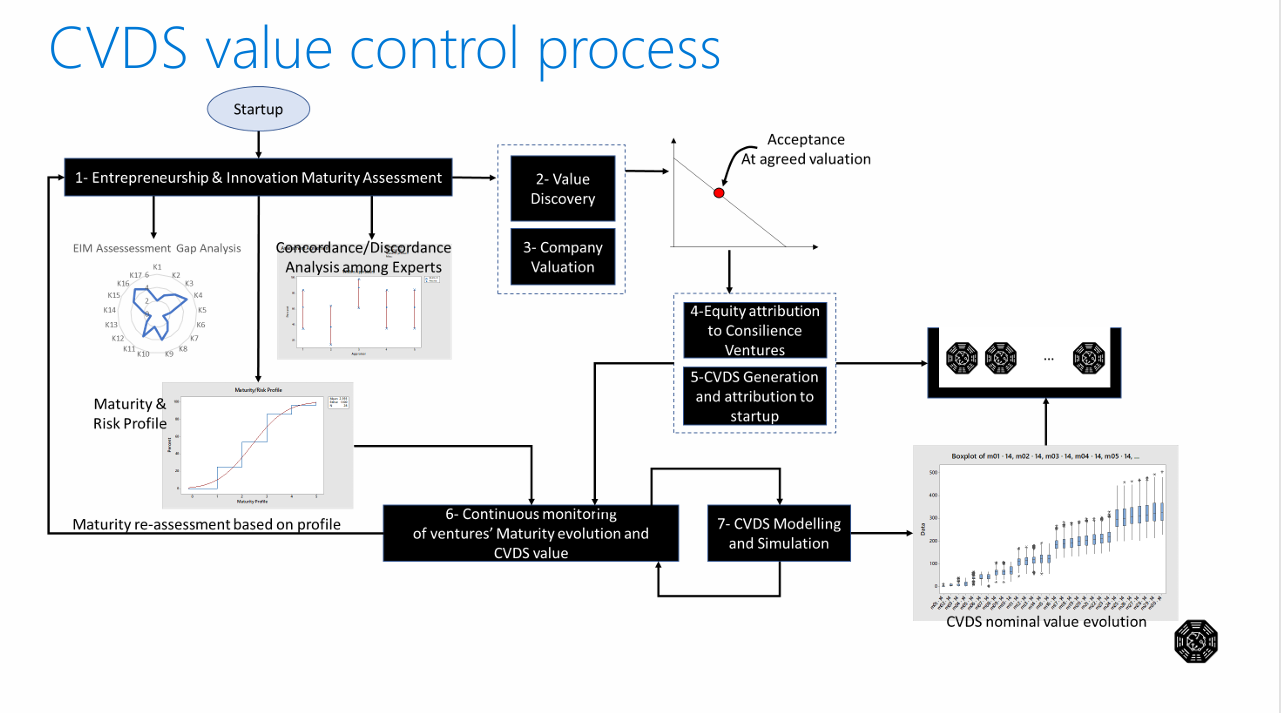
5. Innovation S-Curve Integration
The incorporation of technology lifecycle analysis through Innovation S-curves provides critical insights into:
- Market timing optimization
- Technology adoption phases
- Competitive positioning
- Investment timing strategies
Theoretical Foundation: S-curve analysis, rooted in diffusion of innovations theory, provides predictive capabilities for technology adoption patterns and market development trajectories.
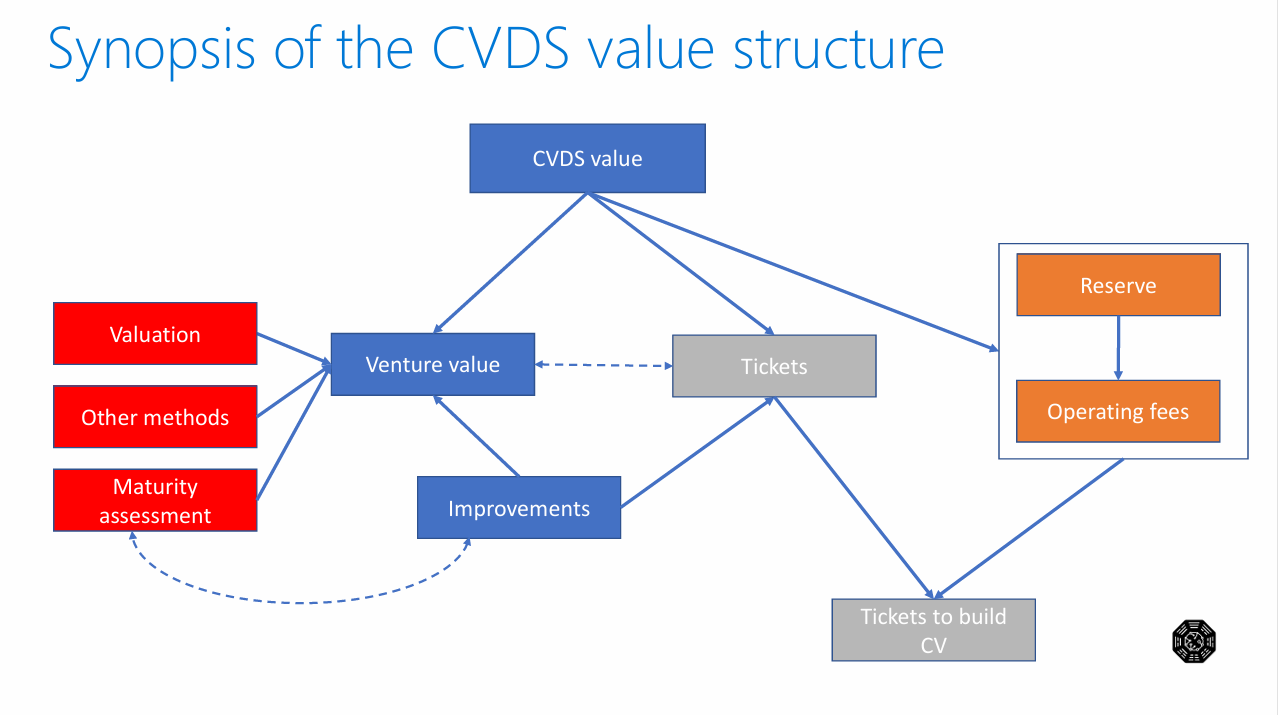
6. Value Structure Architecture
6.1 Hierarchical Value Components
The CVDS value structure incorporates multiple layers:
- Primary Layer: Venture intrinsic value
- Assessment Layer: Maturity and improvement metrics
- Financial Layer: Tickets, reserves, and operating fees
- Portfolio Layer: Diversification and risk management
6.2 Feedback Loop Mechanisms
The system implements closed-loop feedback mechanisms enabling:
- Continuous model refinement
- Performance optimization
- Risk mitigation
- Strategic adaptation
7. Critical Analysis and Limitations
7.1 Strengths
- Holistic Approach: Integration of multiple value dimensions beyond financial metrics
- Dynamic Adaptation: Real-time adjustment capabilities
- Systematic Framework: Structured methodology for complex ecosystem management
- Risk Management: Multi-layered approach to uncertainty management
7.2 Potential Limitations
- Model Complexity: High-dimensional models may suffer from overfitting risks
- Data Dependencies: System effectiveness relies heavily on data quality and availability
- Subjective Elements: Maturity assessments may introduce evaluator bias
- Market Volatility: External market shocks may challenge model stability
8. Scientific Contributions
8.1 Theoretical Innovations
- Integration of organizational maturity models with venture valuation
- Multi-dimensional value function approach
- Dynamic ecosystem health metrics
8.2 Methodological Advances
- Sprint-based capital deployment methodology
- Continuous execution tracking systems
- Technology lifecycle integration in valuation models
9. Implications for Ecosystem Development
The CVDS framework represents a significant advancement in startup ecosystem management by:
- Providing systematic approaches to value creation and assessment
- Enabling data-driven investment decisions
- Facilitating ecosystem optimization through continuous monitoring
- Supporting scalable venture development processes
10. Conclusions
The Consilience Ventures Digital Share framework represents a sophisticated approach to startup ecosystem valuation that addresses traditional limitations through multi-dimensional modeling, continuous assessment, and dynamic adaptation mechanisms. While the complexity of the system presents implementation challenges, the theoretical foundation and methodological rigor suggest significant potential for advancing ecosystem management practices.
The integration of maturity assessment, innovation lifecycle analysis, and dynamic valuation creates a comprehensive framework that could serve as a model for next-generation venture ecosystem management platforms.
References and Further Research Directions
Future research should focus on:
- Empirical validation of model predictions
- Comparative analysis with traditional valuation methods
- Long-term ecosystem performance tracking
- Cross-industry applicability assessment
- Model refinement based on real-world implementation feedback
This analysis is based on the theoretical framework presented in the CVDS documentation and represents an academic interpretation of the proposed valuation methodology.